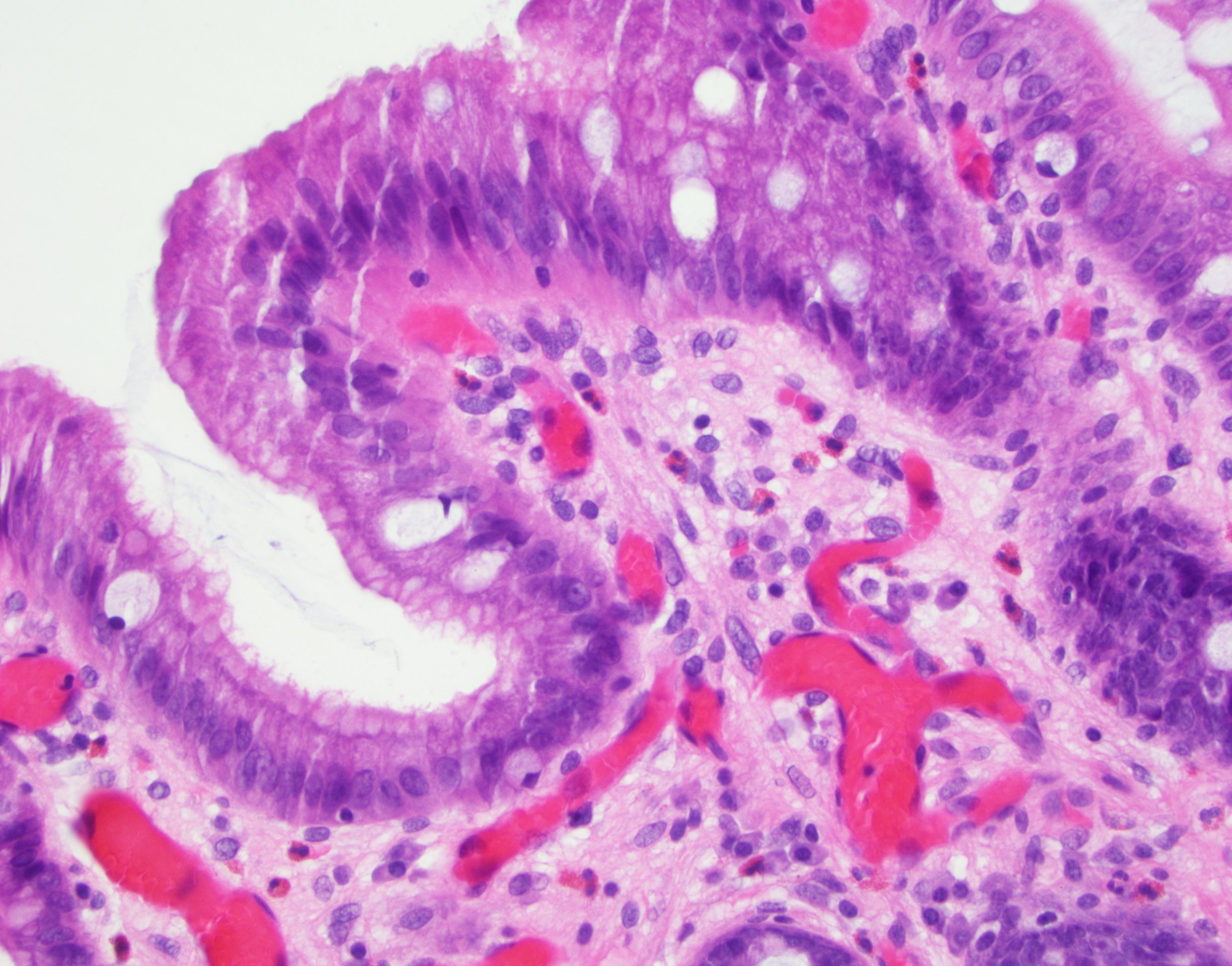
Barrett's Esophagus Histology. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux.
Barrett's Esophagus Histology . Diagnosis Is Made By Clinicans Not Pathologists.
Long Term Nonsurgical Management Of Barrett S Esophagus With High Grade Dysplasia Gastroenterology. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ.
Barrett's esophagus is a condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth to the stomach.
The condition was first described in 1950 by. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. This article details information about symptoms, screening, diagnosis. Barrett's esophagus (be) is characterized as histologic evidence of intestinal metaplasia is pathogenesis of barrett s esophagus. The reason barrett's esophagus is important is because people who have it have a small increased risk of. Free information about barrett's oesophagus. Barrett esophagus (be) is a metaplastic replacement of the stratified squamous epithelium of the distal esophagus with columnar epithelium containing goblet cells. Haoxiang zhang, caifei shen, pu wang, ji feng, yin xu. This occurs in the area where the. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Diagnosis is made by clinicans not pathologists. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. Learn more about barrett's estophagus, including symptoms and causes. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Risk factors for barrett's esophagus and esophageal cancer include having had severe gastroesophageal reflux disease for a long time, being male, and being overweight or obese. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett esophagus is a term for intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus, abbreviated be, is a relatively common pathology of the esophagus, that is associated with an increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Barrett's esophagus is a condition marked by an abnormality in the lining of the lower esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to.
Pathology Outlines Barrett Esophagus : Barrett's Esophagus, Abbreviated Be, Is A Relatively Common Pathology Of The Esophagus, That Is Associated With An Increased Risk Of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma.
Endoscopic Mucosal Ablation And Resection Of Barrett S Esophagus And Related Diseases Munoz Largacha Journal Of Visualized Surgery. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ.
Barrett Esophagus Mayo Clinic Proceedings - Barrett's Esophagus, Abbreviated Be, Is A Relatively Common Pathology Of The Esophagus, That Is Associated With An Increased Risk Of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma.
Role Of Radiofrequency Ablation In Barrett S Esophagus Riegler Annals Of Esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology:
High Yield Gi Pathology Esophagus Gerd Barrett Metaplasia . © 2004 mayo foundation for medical education and research.
Barrett S Esophagus A Comprehensive Review And Update Diagnostic Histopathology. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux.
Barrett S Oesophagus Diagnostic Criteria Endoscopy And Histology Sciencedirect : Barrett's Esophagus Is A Complication Of Chronic Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd).
Barrett S Oesophagus Monitoring Adenocarcinoma Teachmesurgery. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus.
Evaluation Of P53 Protein Expression In Barrett Esophagus Krothapalli M Kini Jr Kini H Sahu Kk Shenoy S Krishna Sg Tantry B V Indian J Pathol Microbiol , It Is Believed To Be Due To Severe, Longstanding, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd).
The Barrett S Gland In Phenotype Space Sciencedirect. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus.
Barrett S Esophagus Nejm : Barrett's Esophagus Is A Condition Affecting The Lining Of The Esophagus, The Swallowing Tube That Carries Foods And Liquids From The Mouth To The Stomach.
Pathology Outlines Barrett Esophagus. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food.
Histopathology Images Of Barrett Metaplasia By Pathpedia Com Pathology E Atlas : Barrett's Esophagus Is A Condition In Which The Flat Pink Lining Of The Swallowing Tube That Connects The Mouth To The Stomach (Esophagus) Becomes Damaged By Acid Reflux, Which Causes The Lining To.
Grading Of Gastric Foveolar Type Dysplasia In Barrett S Esophagus Modern Pathology. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
Biomarkers In Barrett Rsquo S Esophagus And Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Predictors Of Progression And Prognosis . Barrett's Esophagus Is A Condition In Which The Flat Pink Lining Of The Swallowing Tube That Connects The Mouth To The Stomach (Esophagus) Becomes Damaged By Acid Reflux, Which Causes The Lining To.
Barrett S Esophagus 2. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide.
Figure 5 From Barrett Esophagus Histology And Pathology For The Clinician Semantic Scholar , Columnar Epithelium Lined Lower (O).
Barrett S Esophagus Gastroenterologists In Florida. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be;
Barret S Esophagus The Gastrointestinalatlas Gastrointestinalatlas Com - Barrett's Esophagus Is A Complication Of Chronic Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd).
Understanding Barrett S Esophagus. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide.