Barrett's Esophagus Vs Normal Esophagus. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. It is named after the doctor who first described it. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy.
Barrett's Esophagus Vs Normal Esophagus : In Barrett's Oesophagus The Cells That Line The Lower Gullet (Oesophagus) Are Abnormal.
Barrett S Esophagus. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). It is named after the doctor who first described it. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd).
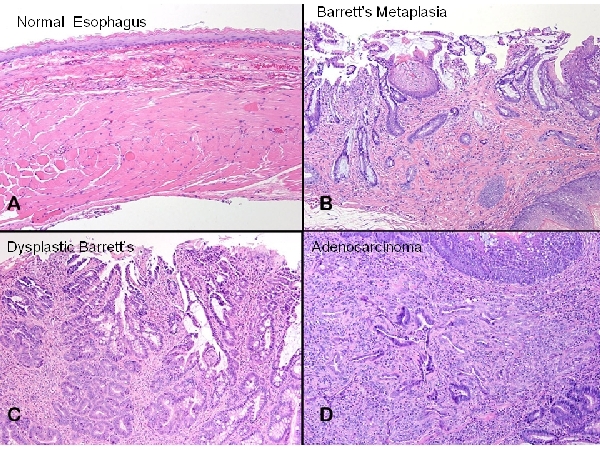
Barrett esophagus is a term for intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus.
Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). Barrett's oesophagus is the asymptomatic replacement of normal squamous epithelium of oesophagus by metaplastic columnar epithelium. Also called barrett's oesophagus, barrett syndrome, barrett esophagus, be, and columnar epithelium lined lower oesophagus, this condition is believed to be a cellular adaptation to gastroesophageal reflux disease, i.e., chronic heartburn. Metaplasia is a process where one type of cell is replaced with another. This altered tissue is similar to that which lines the intestine. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and its complications, particularly barrett's esophagus, is a much favored exam topic. Barrett's esophagus is a change in your cells lining your esophagus (food tube). Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. Pseudogoblet cells may be difficult in some circumstances. Although barrett's esophagus is a precancerous condition, esophageal cancer only develops in about 1 percent of all people with barrett's esophagus. It is considered the precursor lesion for esophageal adenocarcinoma. Management ranges from monitoring your esophageal lining with endoscopies to treatments to remove damaged tissue. The histologic diagnosis of barrett's esophagus in biopsy specimens, in relation to the presence of esophageal glands proper, is discussed. It is named after the doctor who first described it. People with barrett's esophagus may develop a rare cancer called esophageal adenocarcinoma. Treatment for barrett's esophagus ranges from lifestyle changes to medication, or in some cases barrett's esophagus produces symptoms similar to gerd. Barrett esophagus is a term for intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus. In the case of barrett's esophagus, esophageal cells are replaced with. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. There are two kinds of esophageal cancer based on how the cancer cells appear under the microscope: The definition of barrett's esophagus has undergone substantial evolution since norman barrett's original report in of goblet cells vs. If you have barrett's oesophagus, your doctor may recommend you have regular checks for very early signs of cancer. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. This change is called metaplasia. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus.
Barrett S Esophagus Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic , The Esophagus Is The Tube That Connects The Mouth To The Stomach.
Barrett S Esophagus Johns Hopkins Medicine. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. It is named after the doctor who first described it. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies.
Figure 5 From Barrett Esophagus Histology And Pathology For The Clinician Semantic Scholar : While The Prevalence Of Be Is Increasing, The Vast Majority Of Ea Occurs In Patients With Undiagnosed Be.
Barrett S Esophagus Wikipedia. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. It is named after the doctor who first described it. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus.
Barrett S Esophagus Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic : Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium is discussed in detail, including the fact that it is thought to be an intermediate stage between squamous and columnar.
Barrett S Esophagus And Esophageal Cancer An Overview. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. It is named after the doctor who first described it. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus).
Biomarkers In Barrett Rsquo S Esophagus And Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Predictors Of Progression And Prognosis : Thus, Use Of The Term Barrett's Esophagus To Describe Certain Endoscopic Features In The Distal Esophagus Is Inappropriate.
Cureus Barrett S Esophagus A Molecular Overview. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. It is named after the doctor who first described it. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be.
Esophagus Barrett S Esophagus Dysplasia And Adenocarcinoma , Barrett's Esophagus Is The Condition In Which A Metaplastic Columnar Epithelium That Has Both Gastric And Intestinal Features Replaces The Stratified Squamous E.
Hierarchical Clustering Of Genes Selected For Discrimination Of The Download Scientific Diagram. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. It is named after the doctor who first described it. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus.
Barrett S Esophagus Wikipedia : Barrett's Esophagus Occurs When The Normal Lining Of The Esophagus Is Replaced With Different Tissue.
Barrett S Esophagus Wikipedia. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. It is named after the doctor who first described it. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies.
View Of Progression Of Barrett S Esophagus Toward Esophageal Adenocarcinoma An Overview Annals Of Gastroenterology . Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, And Diagnosis.
Barrett S Oesophagus Melbourne Lower Gastrointestinal Tract Treatment Victoria. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. It is named after the doctor who first described it. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus.
Barrett Esophagus Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org , There Are Two Kinds Of Esophageal Cancer Based On How The Cancer Cells Appear Under The Microscope:
Barrett S Esophagus Preventing Progression. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. It is named after the doctor who first described it. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus.
Figure 2 From Barrett Esophagus Histology And Pathology For The Clinician Semantic Scholar . Barrett's Esophagus Occurs When The Normal Lining Of The Esophagus Is Replaced With Different Tissue.
Barrett S Oesophagus For The Histopathologist. It is named after the doctor who first described it. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology.
Understanding Barrett S Esophagus Allied Digestive Health Freehold Nj Gastroenterologist Understanding Barrett S Esophagus Gastroenterologist In Freehold Nj Allied Digestive Health Understanding Barrett S Esophagus Allied Digestive Health : In Barrett's Oesophagus, The Normal Stratified Squamous Layer Of The Oesophagus Is Replaced By Simple Columnar (Glandular) Epithelium (As Present Barrett's Oesophagus Is A Histological Diagnosis.
Esophagus Barrett S Esophagus Dysplasia And Adenocarcinoma. It is named after the doctor who first described it. Background barrett's esophagus (be) is a metaplastic precursor lesion of esophageal adenocarcinoma (ea), the most rapidly increasing cancer in western societies. The aim of this review is to provide an update of the epidemiology. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). While the prevalence of be is increasing, the vast majority of ea occurs in patients with undiagnosed be. It is interesting that the frequency or the intensity of gerd symptoms, such as heartburn, does not affect the likelihood that someone will develop barrett's esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had gerd for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age. In barrett's esophagus, the tissue appears red and velvety. Your doctor will remove tissue (biopsy) from your esophagus. In barrett's oesophagus the cells that line the lower gullet (oesophagus) are abnormal. In barrett's esophagus, the separation is above its normal position. Barrett's oesophagus is a condition which affects the lower gullet (oesophagus). Esophageal ac, on the other hand, can complicate longstanding acid reflux, and the main condition predisposing to its onset is barrett's esophagus (be), an acquired disorder whose prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. Normal esophagus tissue appears pale and glossy. Barrett's esophagus, which is linked to chronic heartburn, can turn into cancer of the esophagus.